Introduction
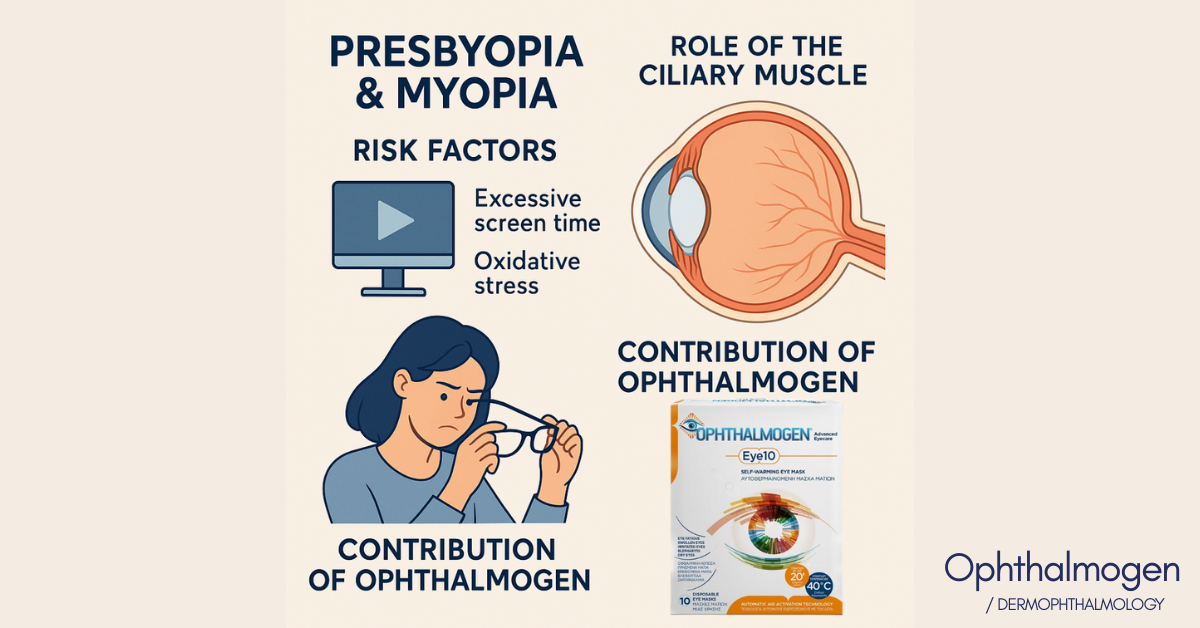
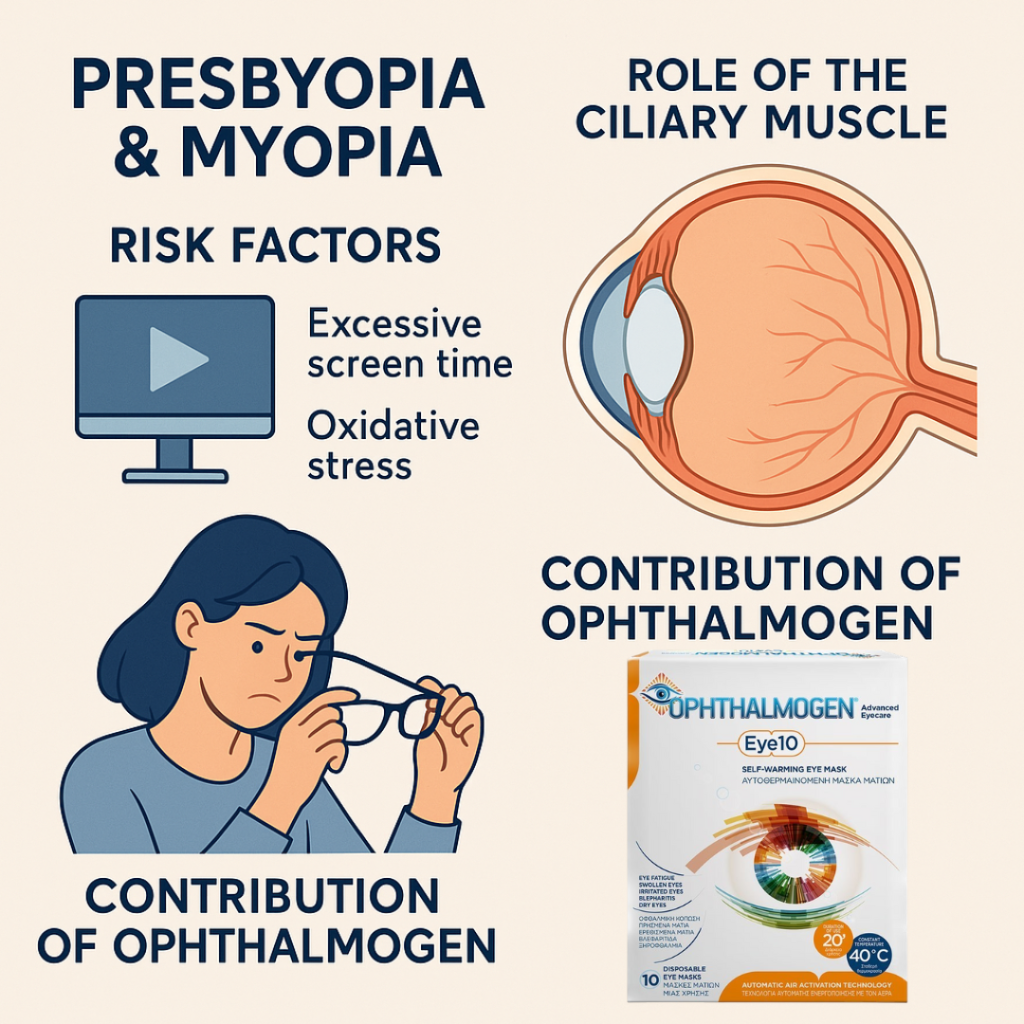
Vision is one of the most precious senses. Even small changes can affect daily life, work, and overall wellbeing. Two of the most common visual conditions worldwide are myopia (nearsightedness) and presbyopia (age-related blurry near vision).
- Myopia usually develops in childhood or adolescence and causes blurry distance vision.
- Presbyopia appears after the age of 40–45, making near tasks such as reading and using a smartphone more difficult.
According to the World Health Organization, more than 50% of the global population will have myopia by 2050, while presbyopia is virtually universal after 45 years of age..
Beyond glasses, contact lenses, or laser surgery, the health of the eyelids and the function of the ciliary muscle – the eye’s focusing muscle – are critical factors in maintaining clear and comfortable vision.
Risk Factors for Myopia
- Genetics – Family history significantly increases risk.
- Environment – Prolonged near work (computers, smartphones, books).
- Lack of outdoor exposure – Children spending less time in natural daylight have a higher risk of developing myopia.
- Accommodative spasm – Continuous contraction of the ciliary muscle due to excessive near work, creating a temporary increase in myopia.

Risk Factors for Presbyopia
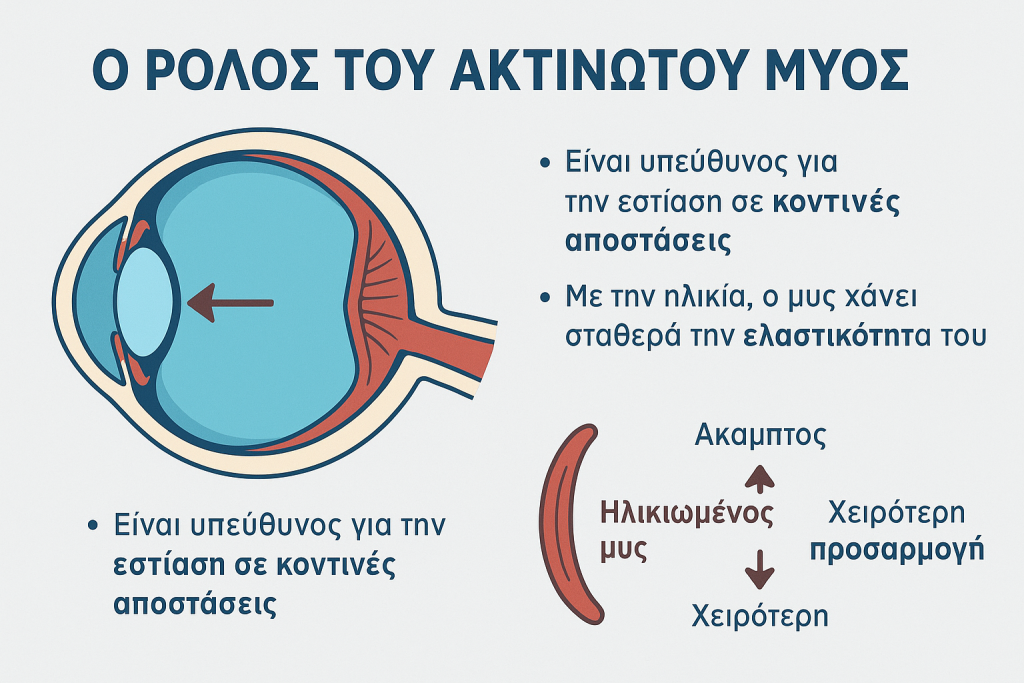
- Age – Natural loss of lens elasticity after 40 years.
- Ciliary muscle dysfunction – Reduced blood flow and flexibility limit the focusing ability.
- Dry eye and visual fatigue – These exacerbate near vision difficulties.
- Hormonal changes – Menopause and other endocrine conditions.
- Systemic diseases – Diabetes and cardiovascular issues that impair circulation.

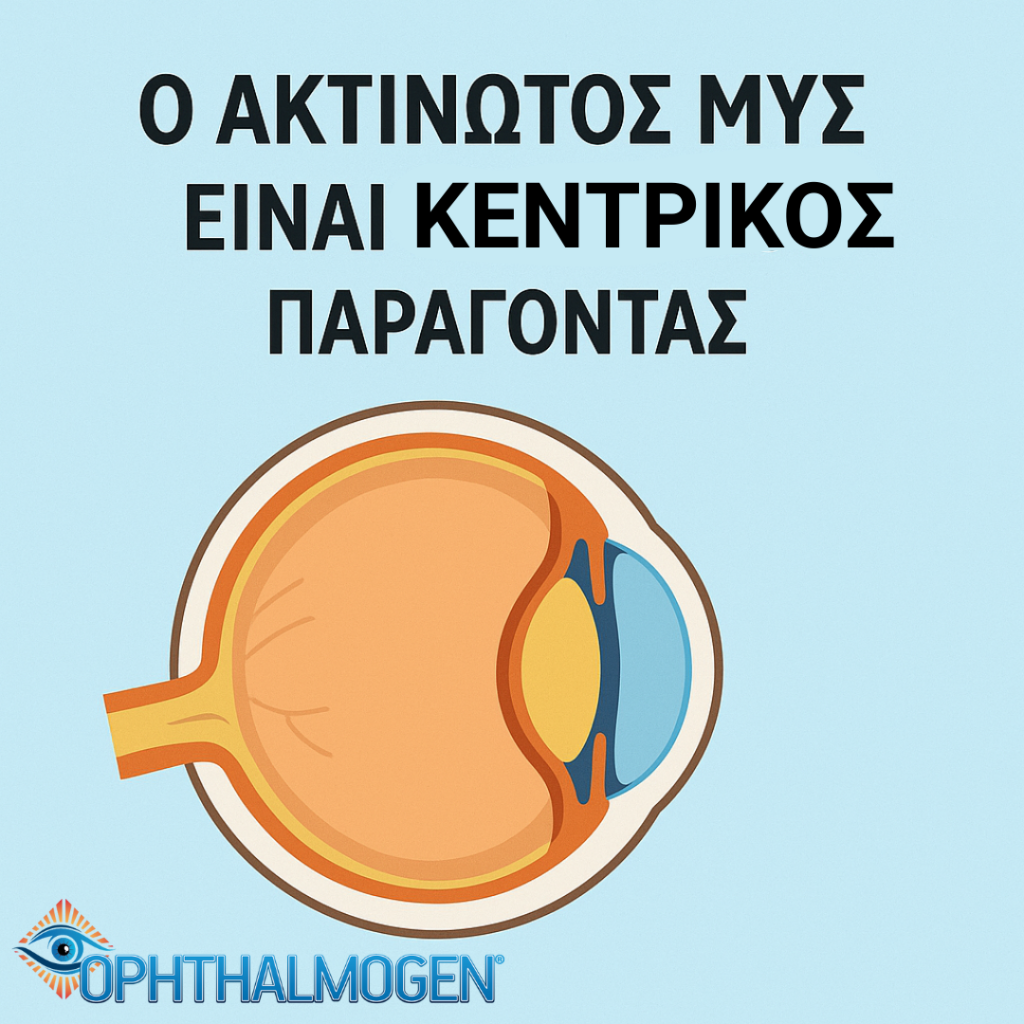
The Role of the Ciliary Muscle
The ciliary muscle is the eye’s focusing mechanism:
- When it contracts → the lens becomes more convex → focus on near objects.
- When it relaxes → the lens flattens → focus on distant objects.
In myopia, overactivity and spasm of the ciliary muscle (due to screen overuse) aggravate the condition.
In presbyopia, loss of lens elasticity combined with reduced muscle endurance and blood supply leads to loss of accommodation.
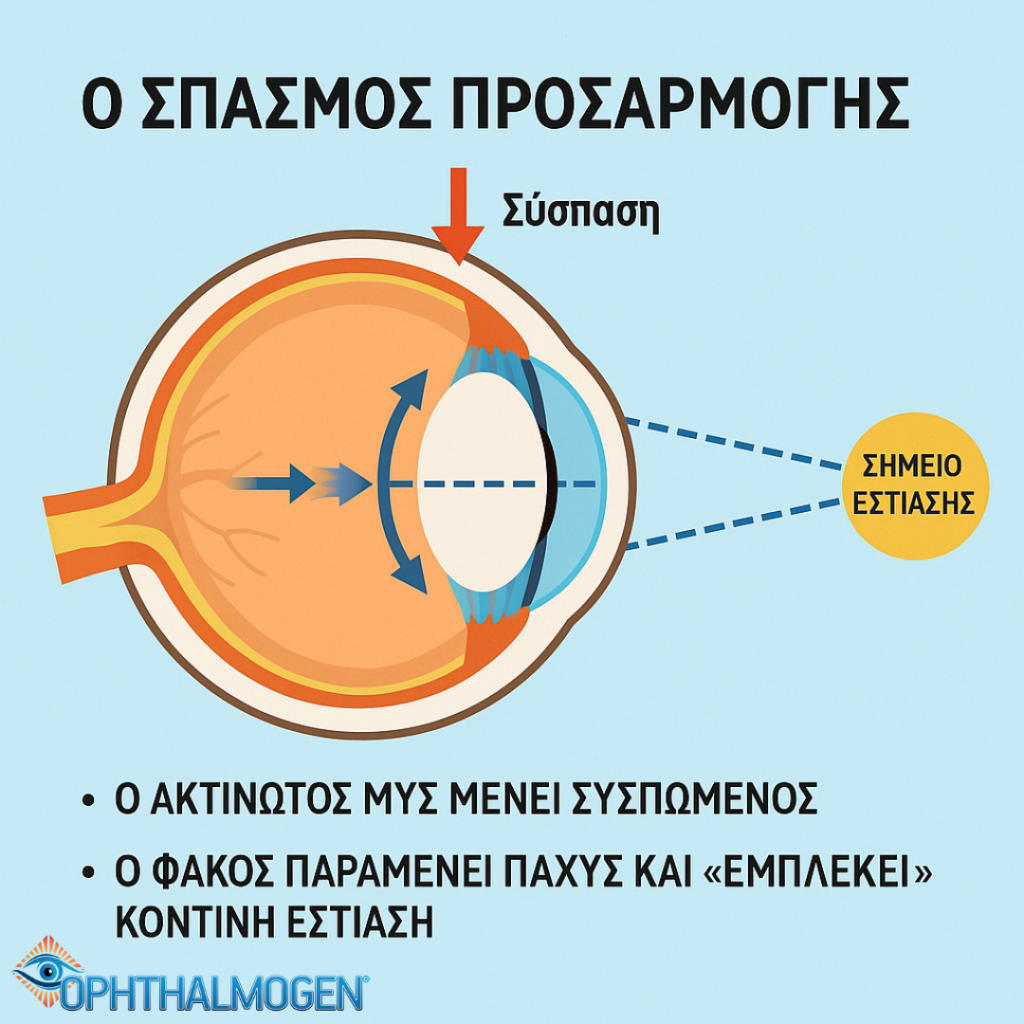
What is Accommodative Spasm?
Accommodative spasm is a functional disorder in which the ciliary muscle remains in continuous contraction due to prolonged near work.
Symptoms include:
- Blurred distance vision (temporary “pseudo-myopia”).
- Headaches and eye fatigue.
- A false impression that “myopia has increased”.
Adequate blood supply and muscle relaxation are essential to reduce this phenomenon..

The Impact of Digital Screens
Our modern lifestyle is dominated by digital screens:
- Prolonged near work is driving a rise in myopia among children and adolescents.
- Presbyopia symptoms are aggravated by digital eye strain and dry eye.
- Constant near focus increases the risk of accommodative spasm.
The 20-20-20 rule is a simple but effective prevention technique: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
New Treatments for Presbyopia
Recent pharmaceutical advances have led to the approval of presbyopia-correcting eye drops, such as pilocarpine (Vuity, Qlosi) and aceclidine (Vizz). These drops improve near vision temporarily by creating a “pinhole effect” through pupil constriction.
- OphthalmogenEYEthe Ophthalmogen EYE10 offers a non-pharmacological, natural and preventive approach that can be used daily without risk..
How Ophthalmogen EYE10 Supports Myopia
- Enhances blood circulation around the eyes.
- Relieves accommodative spasm after hours of screen use.
- Stabilizes the tear film, improving optical quality.
- Provides relief for students and professionals working long hours at a computer.
- Plays a preventive role in children and young adults by reducing the strain of continuous near work.
Usage Protocol – Myopia
- Frequency: Once daily, ideally after prolonged near work.
- Duration: 20 minutes at 40°C.
- After use: Perform 2–3 minutes of near-to-far focus exercises.
- Best for: Students, professionals, people with heavy screen time.

Usage Protocol – Presbyopia
- Frequency: 3–4 times per week (daily if symptoms are significant).
- Duration: 20 minutes at 40°C.
- After use: Read small text without glasses as an exercise for the ciliary muscle.
- Best for: Adults over 40 seeking to delay progression.
The Role of Artificial Tears
- In myopia, they reduce fatigue and improve image clarity.
- In presbyopia, they stabilize the tear film and make near vision more comfortable.
- Complementary to EYE10, they stabilize the tear film
The Role of Ophthalmogen Gel
The Ophthalmogen Gel further enhances the effect of the EYE10 through gentle eyelid massage:
- Stimulates microcirculation and improves blood flow around the ciliary muscle.
- Relieves blockage of the meibomian glands.
- Stabilizes the tear film, ensuring clearer vision.
- Reduces the sensation of heaviness and eye fatigue.
The “Triad of Eye Care”
- Ophthalmogen EYE10 → thermal therapy & circulation.
- Ophthalmogen Gel → eyelid massage & gland relief.
- Artificial tears → hydration of the ocular surface.
Lifestyle & Πρόληψη

- Spend more time outdoors in natural daylight.
- Take regular breaks from screens.
- Stay hydrated and follow a diet rich in antioxidants.
- Practice daily eyelid hygiene with dermophthalmology products.
In Summary
Myopia and presbyopia are conditions that affect millions worldwide and are steadily increasing due to modern lifestyle factors.
The ciliary muscle is central:
- In myopia, accommodative spasm worsens the condition.
- In presbyopia, loss of muscle endurance and lens elasticity reduce near focusing.
- Dermophthalmology and the product line Ophthalmogen offers a comprehensive solution:
- The EYE10 with thermotherapy 40°C.
- Gel for eyelid massage and gland health.
- Artificial tears for hydration.
This is a preventive, non-invasive, daily routine for healthier, clearer and more comfortable vision at every age.
Give your eyes the care they deserve!
Discover the new era of eye and skin care at www.dermophthalmology.com