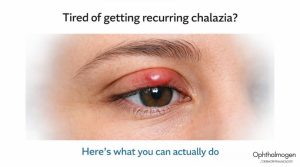
Introduction – The Dual Nature of the Eyelash
Eyelashes are among the most delicate and expressive structures of the human face.They symbolize beauty and youth, yet at the same time act as aerodynamic filters and protective sensory barriers for the eyes.In today’s era of extensions, mascara, and heavy makeup, aesthetics often override physiology.
Dermophthalmology restores balance — merging Ophthalmology, Dermatology, and Trichology to show that the beauty of the eyes begins with their health.
Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Eyelash
An eyelash is a keratinized hair shaft growing along the eyelid margin.
An eyelash is a keratinized hair shaft growing along the eyelid margin.
- A root surrounded by a follicle,
- Zeis glands (sebaceous) and Moll glands (sweat) providing lubrication,
- Zeis glands (sebaceous) and Moll glands (sweat) providing lubrication,
- Meibomian glands, located deeper in the tarsal plate, secreting lipids for the tear film.
Its life cycle lasts 4–11 months, passing through:
- Anagen (growth),
- Catagen (regression),
- Telogen (resting).
The follicle’s dermal papilla regulates regeneration and growth rate, while eyelash keratin is denser and more curved than that of the scalp — designed for flexibility and endurance. The Zeis–Moll lipid micro-layer acts as a “lubrication system” reducing friction between eyelid and cornea.Thus, the eyelash is not just hair — it is a functional sensory organ with nerve endings triggering blink reflexes for ocular defense.
Trueb RM, Int J Trichology, 2010 · Bolognia JL, Dermatology, 2018 · Dawber R, Hair and Scalp Disorders, 2012
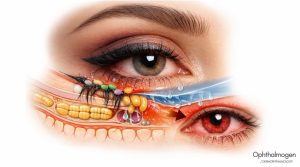
The Meibomian Glands – The Hidden Partner of the Lashes
The Meibomian glands form the core of the eye’s lipid homeostasis.
Their secretion:
- lubricates the lash roots,
- minimizes eyelid friction,
- prevents tear-film evaporation.
Each eyelash operates within a microenvironment of Zeis, Moll, and Meibomian glands — an integrated Meibomian–Follicle Axis that maintains visual stability.
- the hair follicle,
- the Zeis/Moll glands,
- and the Meibomian glands work in coordination.
Inflammation or obstruction in any component disrupts the entire system.
Knop E et al., Exp Eye Res, 2011 · Nichols JJ, Ocul Surf, 2012 · Periman L, Ocul Surf, 2023
The Six Primary Eyelash Disorders
Dermophthalmology recognizes that lash disorders belong simultaneously to Ophthalmology, Dermatology, and Trichology.
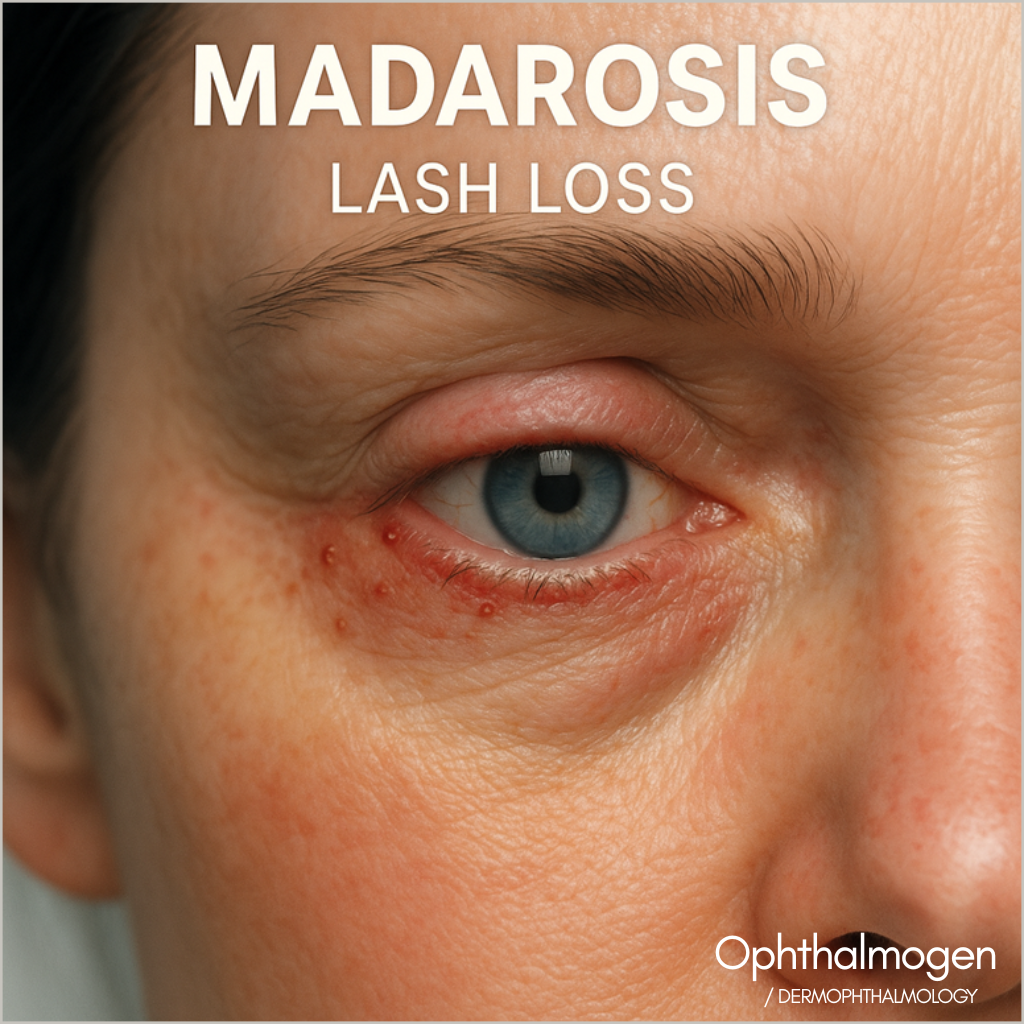
- Madarosis – Lash Loss
Inflammatory or autoimmune follicular damage causing eyelash loss.Associated with blepharitis, rosacea, psoriasis, folliculitis, and Demodex infestation.Loss of lashes compromises barrier integrity, leading to dryness and photosensitivity. Knop et al., Exp Eye Res, 2011
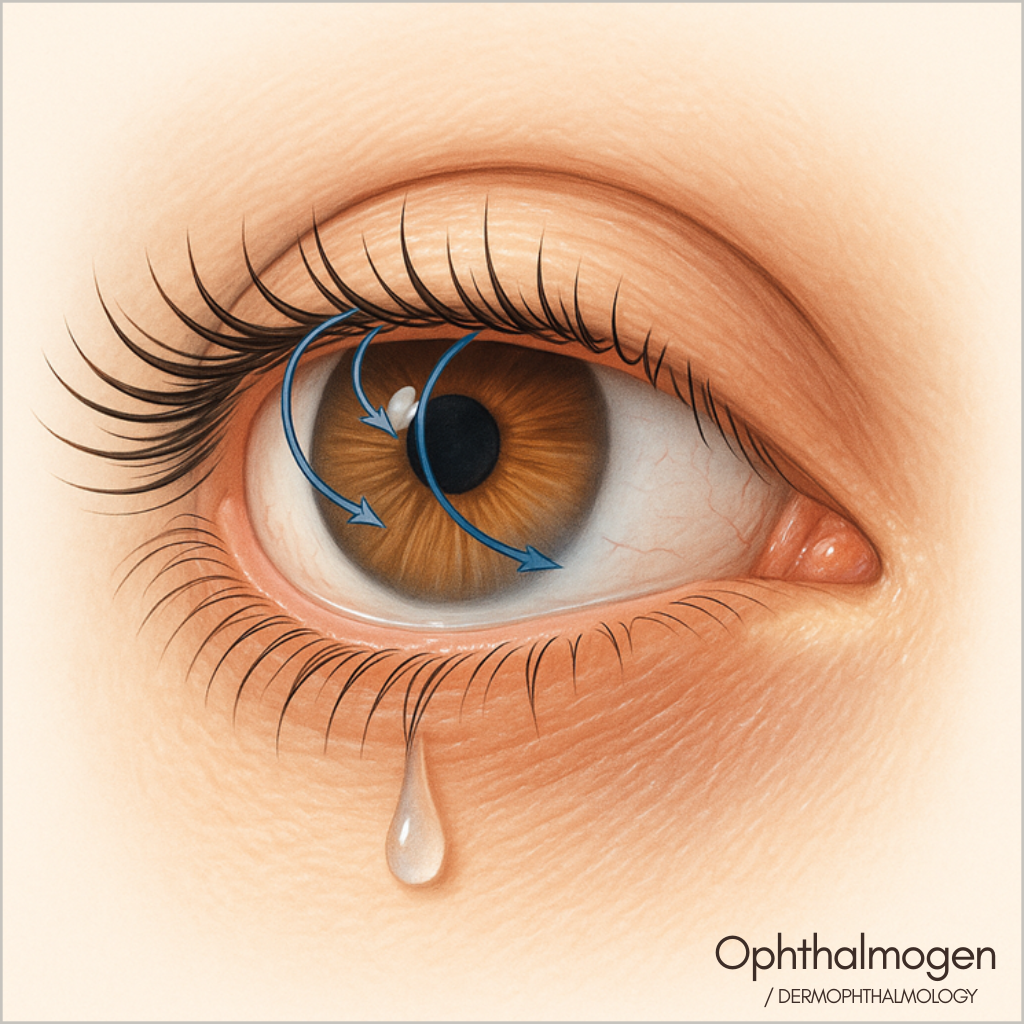
- Trichiasis– Inward-Growing Lashes
- Distichiasis – Secondary Lash Row
A second row of lashes emerging from Meibomian ducts; causes microtrauma and ocular surface irritation.May be congenital or acquired following chronic MGD.
McDonald MB et al., Cornea, 2018
- Poliosis (Poliosis)
A second row of lashes emerging from Meibomian ducts; causes microtrauma and ocular surface irritation.May be congenital or acquired following chronic MGD.
et al., Dermatology, 2013
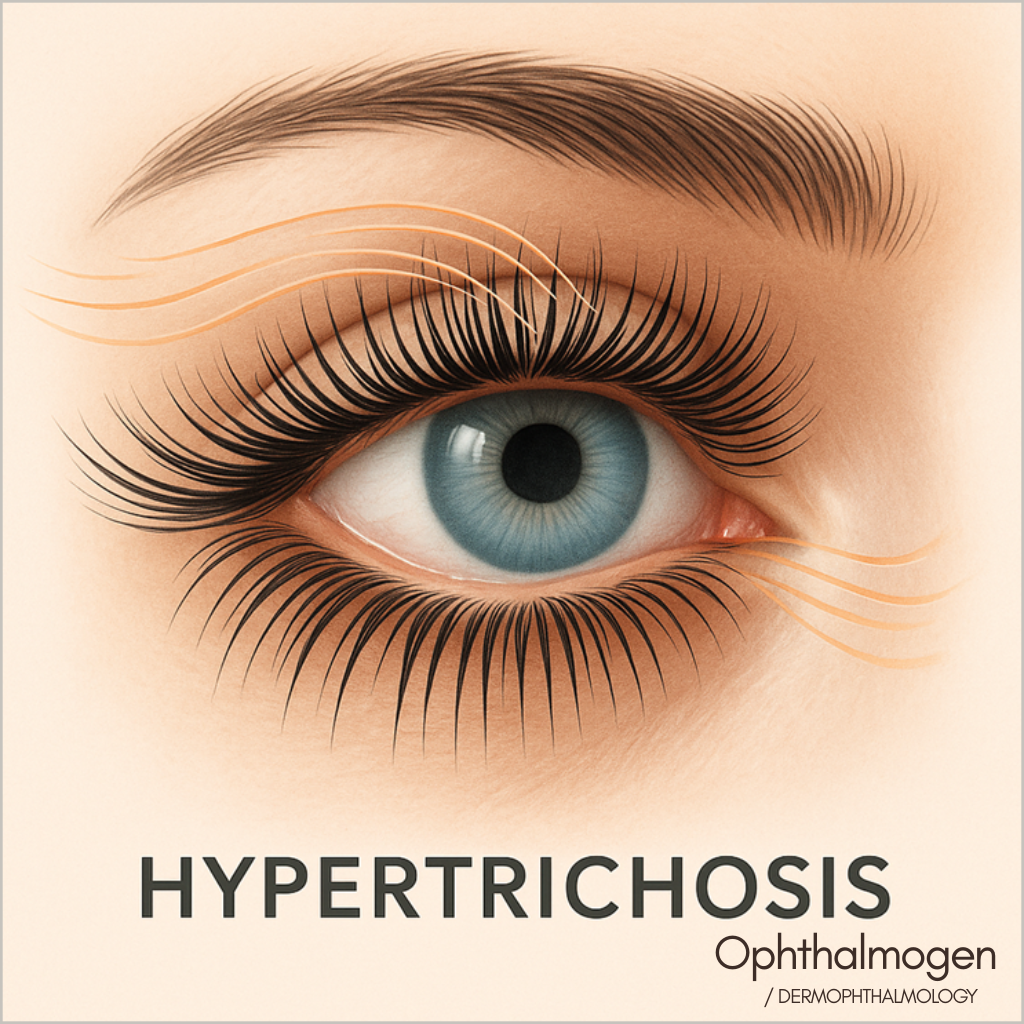
- Hypertrichosis – Excessive Growth
Induced by prostaglandins, hormonal shifts, or inflammation.Abnormally dense lashes alter airflow, increasing tear evaporation and irritation.
Galor et al., Ocul Surf, 2020
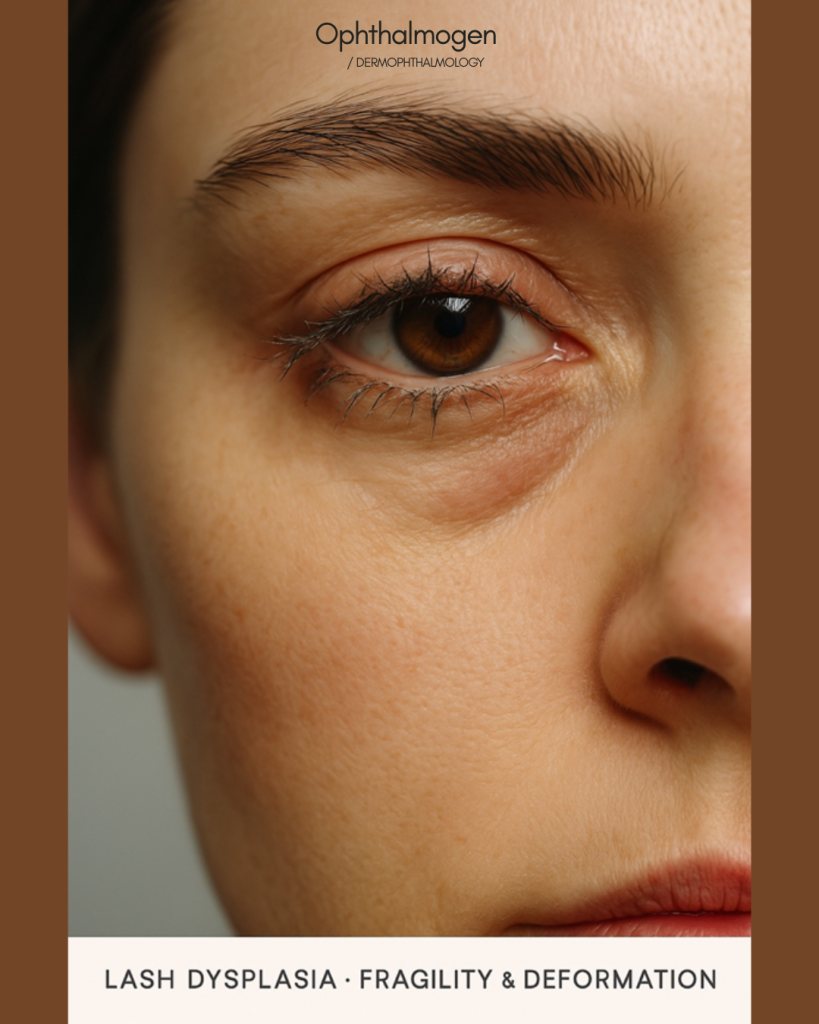

- Lash Dysplasia– Fragility & Deformation.)
Induced by prostaglandins, hormonal shifts, or inflammation.Abnormally dense lashes alter airflow, increasing tear evaporation and irritation.
Matsumoto et al., Cornea, 2018
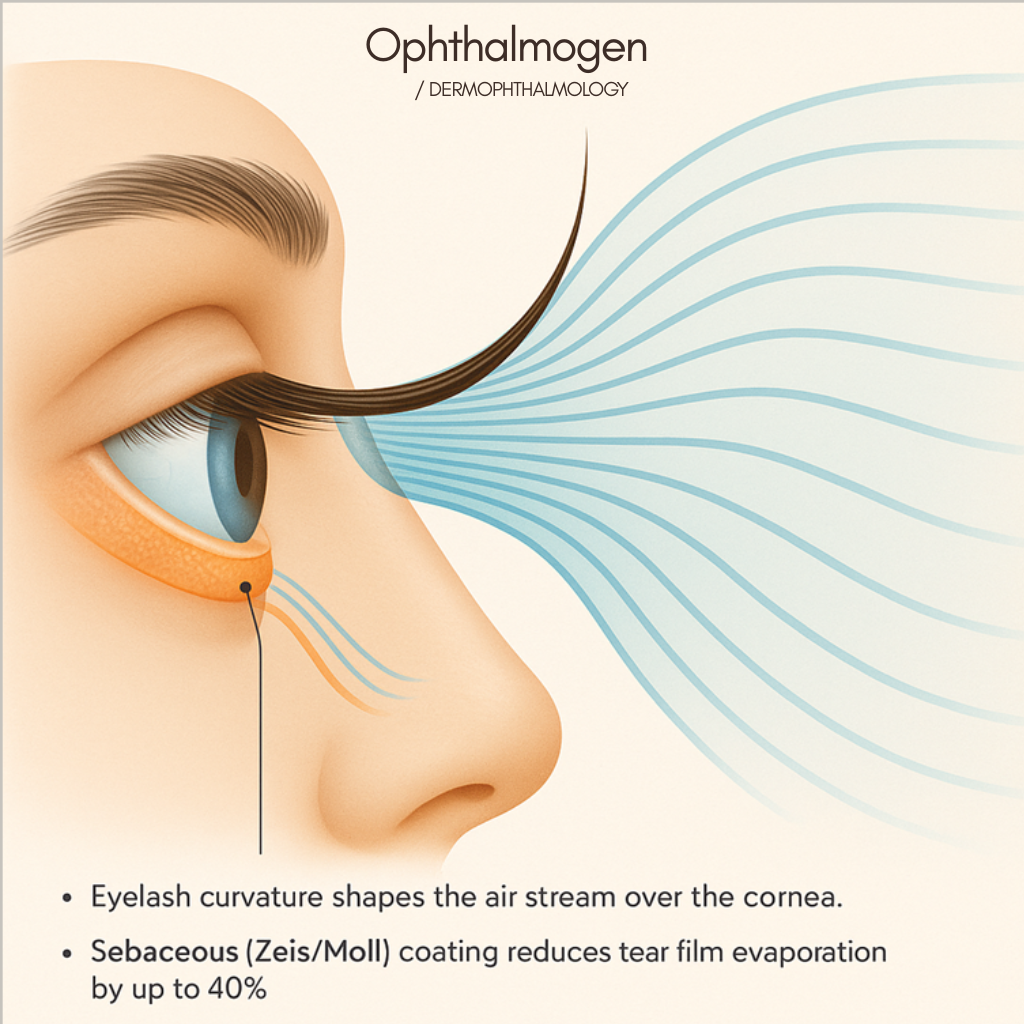
The Aerodynamics of the Gaze – “Air-Tunneling Effect”
Hu & Mitchell (2015) showed that eyelashes reduce tear evaporation by up to 50% when their length equals one-third of the eye opening.This proportion creates a low-flow chamber that shields the cornea from airflow and dust.Altered curvature or length (due to cosmetics or extensions) breaks this natural shield, triggering dry-eye and ocular fatigue.Hu & Mitchell, J R Soc Interface, 2015

LashLoss → Ocular Dryness Pathway
Dermo-Ophthalmology describes a characteristic pathophysiological “pathway”:
- Inflammation &Zeis/Moll blockage → lipid barrier loss.
- Reduced blink rate → faster tear evaporation.
- Meibomian dysfunction → chronic inflammation.
- Corneal irritation → redness, tearing, blurred vision.
Σε απλά λόγια:lash loss → ocular dryness → blurred vision.
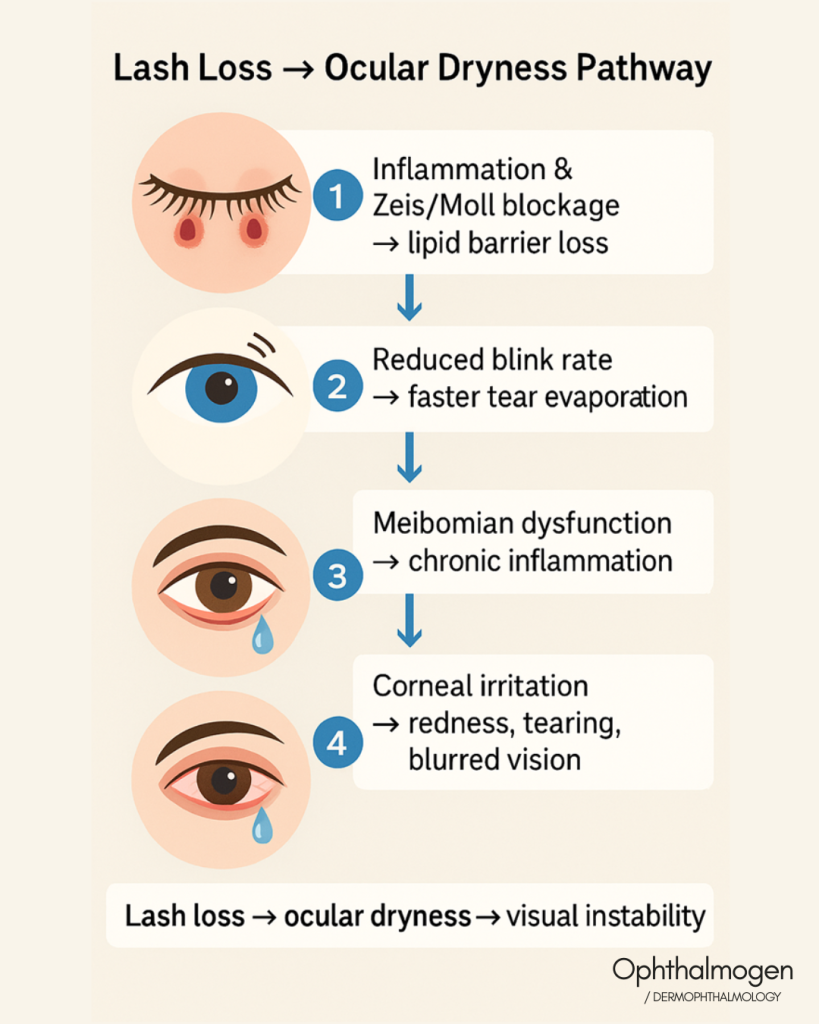
Lash loss → ocular dryness → visual instability.

Lashes evolved in mammals as anti-desiccation structures regulating ocular humidity.In ancient Greek medicine, Hippocrates (in Peri Ophthalmon) described eyelid hair cleansing as essential to eye health — 25 centuries before TFOS DEWS II.In medieval times, lash loss signified inner illness.In modern times, aesthetics overshadowed function, often at the cost of ocular surface integrity.
Hippocrates, Peri Ophthalmon; Hu & Mitchell, 2015; Paus &Cotsarelis, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 1999
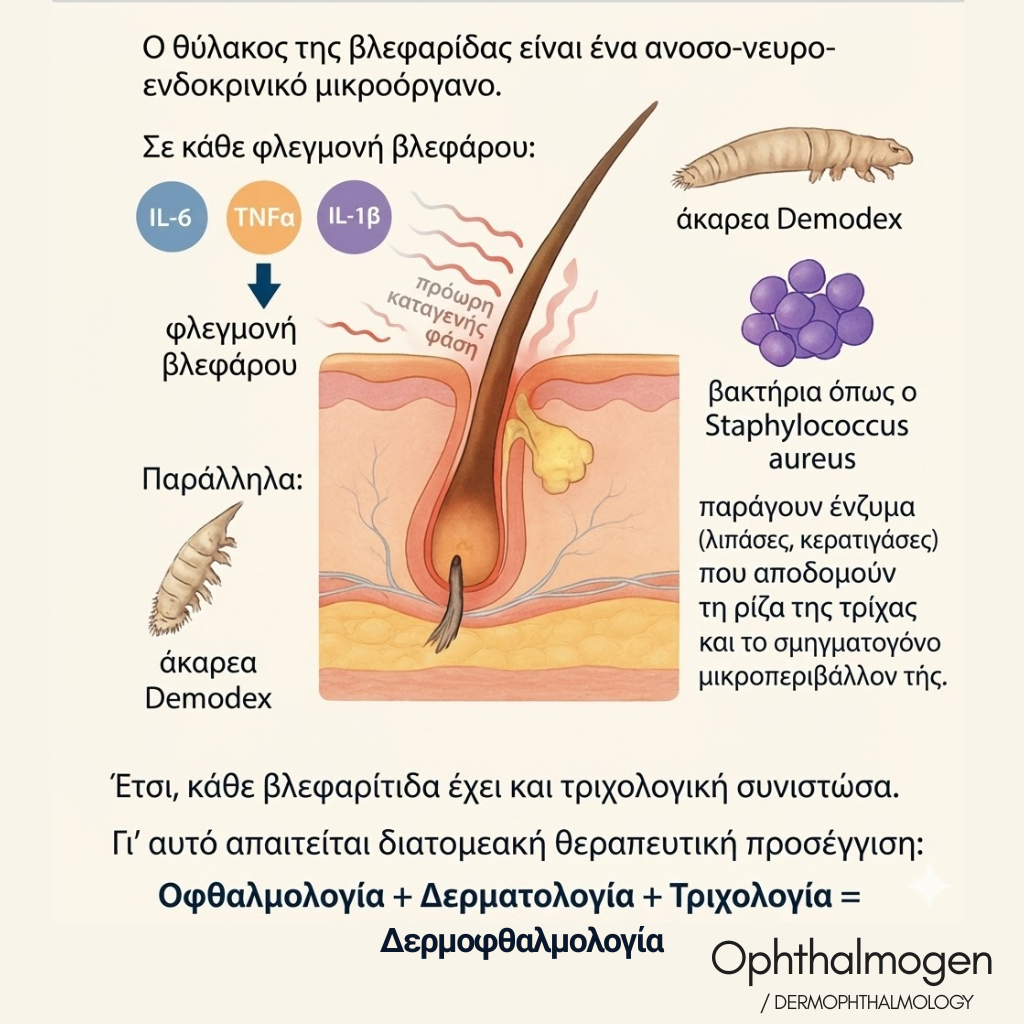
Trichologic Pathophysiology of Ocular Inflammation
The lash follicle is an immuno–neuro–endocrine micro-organ.Inflammation activates cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α), causing premature catagen — early shedding phase.Demodex mites and Staphylococcus aureus secrete lipases and keratinases that degrade the lash root and lipid layer.Hence, every blepharitis is also a trichologic disorder — requiring interdisciplinary care.
Paus R, Exp Dermatol, 2011; Periman L, Ocul Surf, 2023; McDonald MB, Cornea, 2018
Biomechanics & Tear Interaction
The cilia are not passive structures – they actively influence airflow and tear evaporation:
- The curvature of the eyelash shapes the airflow in front of the cornea.
- Zeis/Moll lipid coating reduces tear film evaporation by up to 40%.
- Loss of elasticity or deformation (from mascara, extensions, glues, etc.) alters the flow and causes over-evaporation.
- The studies Mitchelletal., 2015 and Pult&Nichols, 2012 confirm that the “aerodynamics” of the gaze depends on the length, thickness and angle of the eyelashes.
In other words: any change in the trichological structure of the eyelash is also a change in ocular physiology.
The Ophthalmoderma – The Unified Eye–Skin Ecosystem
Ophthalmoderma unites eyelid, lashes, brows, and periocular skin in one functional ecosystem.Inflammation affects both vision and facial expression.Dermophthalmology promotes collaboration between ophthalmologists, dermatologists, and beauty professionals for prevention and safe care.
The Role of Beauticians and Makeup Artists
Lash artists and aestheticians are often the first to notice:
- come into direct contact with eyelashes, eyelids and periorbital skin every day,
- are often the first to notice:
- irritation,
- Madarosis,
- scales
- dryness
- changes in the density and texture of eyelashes.
Their information about:
- eyelid hygiene,
- “clean eye beauty” products,
- and safe make-up & extensions techniques,
It contributes significantly to the prevention of diseases and the preservation of the natural beauty of the eyes.
However, the diagnosis and treatment of pathological conditions (blepharitis, madarosis, trichiasis, gland inflammation, etc.) belong exclusively to the ophthalmologist.
The collaboration of beautician - makeup artist - ophthalmologist - dermatologist forms the basis of the new holistic approach "EyeHealth&BeautySynergy": first health and cleanliness, then aesthetic enhancement.

Practical “Lash Health Routine”
Daily Cleansing:
Ophthalmogen Gel/Foam (Tea Tree Oil + Hyaluronic Acid).
Thermotherapy:
Ophthalmogen Eye10 (40°C for 20’) to clear Meibomian ducts.
Hydration:
Ophthalmogen Spray/Mist for ocular–dermal balance.
Prevention of abuse
Avoid heavy cosmetics that obstruct gland openings.
proper make-up removal,
judicious use of extensions.
New concept: “CleanEyeBeauty” — beauty through health.
Scientific Foundations
- Ophthalmology:
McDonald MB et al., Cornea (2018) · Nichols JJ et al., Contact Lens Anterior Eye (2012)
- Dermatology:
Schallreuter et al., Dermatology (2013) · Periman L. et al., Ocul Surf (2023)
- Trichology:
Trueb RM, Int J Trichology (2010) · Bolognia JL, Dermatology (2018) · Dawber R., Hair and Scalp Disorders (2012)
- Dermophthalmology:
Tsakalos J. et al., The Ophthalmodermal Interface – World Organization of Dermophthalmology
Significance of This Article
This paper represents the first international synthesis of Ophthalmology,
- Ophthalmology,
- Dermatology
- and Trichology
the role of eyelashes in vision, health, and beauty.
It establishes:
- eyelashes as functional sensory organs,
- the Meibomian–Follicle Axis as a cornerstone of ocular stability,
- and Dermophthalmology as the new medical framework for integrated eye–skin care.
John Tsakalos
CEO Breath Purity / Ophthalmogen
Founder of the Dermophthalmology Concept
Conceived in Greece